Blog
Shilajit Side Effects & Precautions: Must-Know Risks!

Shilajit, often dubbed the “conqueror of mountains” in Ayurvedic lore, is a sticky, tar-like resin found in high-altitude regions like the Himalayas and Altai Mountains, where it’s sometimes called Altay mummiyo. Packed with minerals, fulvic acid, and humic acid, it’s been celebrated for centuries for boosting energy, enhancing stamina, and supporting overall health. But before you add this potent supplement to your routine, you need to know the full story, its benefits, potential side effects, and critical precautions.
Keep reading to find out everything you need to know about shilajit and its impact on your body!

Quick information:
Aspect | Details |
What is Shilajit? | A mineral-rich resin from mountain rocks, used in Ayurveda for vitality. |
Key Benefits | Boosts energy, supports fertility, enhances cognition, strengthens bones. |
Safe Dosage | 200–500 mg daily, ideally with medical guidance. |
Potential Side Effects | Nausea, low blood sugar, allergic reactions, heavy metal toxicity. |
Precautions | Avoid during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or with certain medications. |
Best Time to Take | Morning or early afternoon with water or milk for optimal absorption. |
Halal Status | Generally halal, but confirm purity and processing methods. |
What Is Shilajit and Why’s It So Popular?
Imagine a dark, resinous substance seeping from ancient mountain rocks, formed over centuries from decomposed plants and minerals. That’s shilajit, or Altay mummiyo, a natural powerhouse loaded with over 80 minerals, fulvic acid, and humic acid. In Ayurveda, it’s revered for boosting energy, improving male fertility, and enhancing brain function. Today, it’s a darling of the wellness world, with fans praising its ability to fight fatigue, support bone health, and act as an antioxidant.
But let’s keep it real—while shilajit’s benefits are exciting, the science is still catching up. Studies, like one from 2010 in Andrologia, show it can improve sperm count and testosterone, but broader claims like anti-aging or Alzheimer’s prevention need more human research. So, before you dive in, let’s explore the safety side.
Is Shilajit Safe for Daily Use?
When purified and taken in moderation, shilajit is generally safe for most healthy adults. Research, including a 2012 rat study, suggests doses up to 5,000 mg/kg for 91 days showed no major toxicity. For humans, 200–500 mg daily for 8–48 weeks is typically well-tolerated. But here’s the deal:
- Purity is non-negotiable: Unprocessed shilajit can harbor heavy metals like lead or arsenic, which can wreak havoc on your health.
- Your body, your rules: Everyone reacts differently. Start with a low dose (200 mg) and see how you feel.
- Doctor’s orders: If you have conditions like diabetes or heart issues, check with a healthcare provider first.
Choose lab-tested, purified shilajit from reputable brands to minimize risks.
Can You Overdo Shilajit?
Absolutely, and going overboard isn’t a vibe. Exceeding the recommended 200–500 mg daily dose can lead to trouble, including:
- Stomach woes: Nausea, diarrhea, or cramps, especially if taken on an empty stomach.
- Low blood sugar: Shilajit can drop glucose levels, risky for diabetics or those on meds.
- Dizziness or overheating: Its warming effect can cause dehydration or lightheadedness if you overdo it.
Stick to the advised dose, and don’t think more equals better. A 2020 study found no adverse effects at recommended doses, but pushing limits isn’t worth the risk.
What Side Effects Should You Watch For?
Shilajit is generally well-tolerated, but it’s not perfect. Here are the potential side effects to keep on your radar:
- Digestive issues: Nausea, upset stomach, or diarrhea, especially with high doses or impure products.
- Allergic reactions: Rare but serious—think rashes, itching, or breathing trouble. Stop immediately if these hit.
- Low blood pressure: Risky for those already on hypertension meds or with low BP.
- Increased uric acid: Bad news for gout sufferers, as it could trigger flare-ups.
- Heavy metal toxicity: Unpurified shilajit might contain lead, arsenic, or mercury, leading to serious health issues.
Always opt for third-party tested products and monitor your body’s response.

Does Shilajit Mess with Medications?
Shilajit’s bioactive compounds, like fulvic acid, can interact with certain medications, so proceed with caution:
- Diabetes drugs: Shilajit may amplify insulin or metformin, risking hypoglycemia. Monitor blood sugar closely.
- Blood pressure meds: It can lower BP, potentially causing dizziness when paired with drugs like amlodipine.
- Blood thinners: Its mineral content might interfere with drugs like warfarin, affecting clotting.
- Statins: Shilajit’s cholesterol-lowering effects could enhance statins, requiring dose adjustments.
Always loop in your doctor if you’re on meds to avoid surprises.
Is Shilajit Risky for Some People?
Shilajit isn’t a one-size-fits-all supplement. Certain groups should avoid it or tread carefully:
- Hemochromatosis patients: High iron content can worsen iron overload.
- Low blood pressure folks: Risk of dizziness or fainting.
- Diabetics: Potential for dangerously low blood sugar.
- Gout sufferers: Increased uric acid could spark painful flare-ups.
- Autoimmune conditions: Shilajit’s immune-boosting effects might worsen lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Pre-surgery: Stop at least two weeks before to avoid blood sugar or pressure issues.
If you’re in one of these groups, talk to a doctor first.
Can You Use Shilajit While Breastfeeding?
Shilajit and breastfeeding are a risky combo. There’s no solid research proving it’s safe for moms or babies, and its bioactive compounds could pass through breast milk, potentially affecting infant development or hormone levels. Contaminated shilajit also poses a heavy metal risk.
- The safe move: Skip shilajit while breastfeeding unless your doctor explicitly approves.
- Alternatives: Stick to nutrient-dense foods or doctor-recommended supplements like prenatal vitamins.
Wait until breastfeeding is over and consult a healthcare provider before starting.
Is Shilajit Halal?
Wondering, “Is shilajit halal?” Good news: it’s typically considered halal since it’s a natural resin from rocks, not animals. But there’s a catch:
- Verify purity: Some brands use non-halal processing agents like alcohol or gelatin capsules.
- Choose wisely: Look for halal-certified products or vegan capsules to be sure.
Check labels and contact manufacturers to confirm compliance with halal standards.
When’s the Best Time to Take Shilajit?
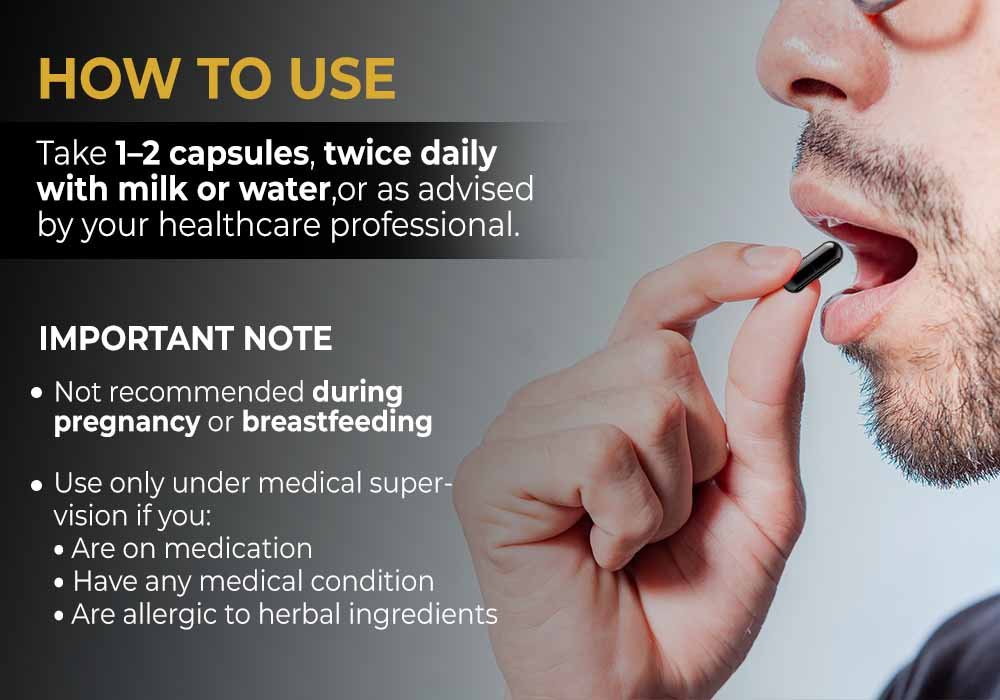
Timing can maximize shilajit’s benefits. Here’s the breakdown:
- Morning: Take 200–500 mg with warm water or milk to kickstart energy.
- Early afternoon: A dose before lunch can combat midday fatigue.
- Skip evenings: Its stimulating effects might disrupt sleep.
How to take it:
- Resin: Dissolve a pea-sized amount in warm liquid.
- Capsules: Follow the label, ideally with food.
- Powder: Blend into smoothies or yogurt to mask its earthy taste.
Consistency matters, but don’t exceed two doses daily.
Can Sea Moss and Shilajit Be Combined?
Sea moss and shilajit are both mineral-rich superstars, but can they play nice together? Sea moss, packed with iodine and trace minerals, could complement shilajit’s energy-boosting effects, potentially supporting thyroid health and vitality. But here’s the deal:
- Ease in slowly: Start with one supplement to gauge your body’s response.
- Avoid overload: Both are mineral-heavy, so overdoing it risks imbalances.
- Check with a doc: Ensure the combo won’t clash with your health or meds.
Try taking shilajit in the morning and sea moss later to spread out nutrient absorption.
What Makes Shilajit by Bodywise Stand Out?
Shilajit by Bodywise is a popular choice, marketed as a high-quality, purified supplement in capsule form for easy use. Here’s the scoop:
- Pros: Lab-tested for purity, reducing heavy metal risks. Capsules are tasteless, unlike raw resin.
- Cons: Pricier than some alternatives, and benefits require consistent use.
- Dosage: Typically 300–500 mg daily, but follow the label or your doctor’s advice.
Compare it with other brands, ensuring third-party testing for safety.
What Are the Biggest Myths About Shilajit?
Shilajit is shrouded in misconceptions that can mislead users. Let’s debunk the top ones:
- Myth: Shilajit cures everything.
- Truth: It’s a supplement, not a magic bullet. Claims like Alzheimer’s prevention lack robust evidence.
- Myth: More shilajit equals more benefits.
- Truth: Overdosing increases side effect risks without extra perks.
- Myth: Raw shilajit is superior.
- Truth: Unprocessed shilajit can contain harmful toxins. Always choose purified forms.
- Myth: Effects are instant.
- Truth: Benefits, like improved energy, build over weeks with regular use.
Stick to facts and avoid falling for exaggerated claims.
Shilajit Safety Precautions
- Not suitable for pregnant and breastfeeding women due to lack of research.
- May lower blood sugar levels, potentially dangerous for people with diabetes.
- May interfere with blood sugar control during and after surgery.
- May lower blood pressure, risky for hypertension medication users or those with existing heart conditions.
- May worsen autoimmune diseases like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
- People with these conditions should avoid shilajit.
Your Burning Questions Answered: Shilajit Insights
Q: Can shilajit cause weight gain?
A: Unlikely. It may support metabolism, but overeating while using it could lead to weight gain.
Q: Is it safe for kids?
A: No. There’s no research on its safety for children, so avoid it.
Q: Does shilajit expire?
Q: Is shilajit safe for women?
Conclusion: What’s Next for Your Shilajit Journey?
Shilajit can be a powerful addition to your wellness routine, offering benefits like boosted energy, better stamina, and potential fertility support. But it’s not without risks—side effects like nausea, low blood sugar, or heavy metal exposure from impure sources are real concerns. By choosing purified shilajit, sticking to 200–500 mg daily, and consulting a doctor, you can use it safely. Whether you’re eyeing Shilajit by Bodywise or combining it with sea moss, always prioritize quality and caution.
This is just the start! Our next blog will explore shilajit’s top benefits and compare it to other superfoods like ashwagandha and spirulina. Curious about which natural supplements can elevate your health without the risks? Stay tuned for more!













